CUQIpy’s Documentation#
CUQIpy stands for Computational Uncertainty Quantification for Inverse Problems in python. It’s a robust Python package designed for modeling and solving inverse problems using Bayesian inference. Here’s what it brings to the table:
A straightforward high-level interface for UQ analysis.
Complete control over the models and methods.
An array of predefined distributions, samplers, models, and test problems.
Easy extendability for your unique needs.
A number of CUQIpy Plugins are available as separate packages that expand the functionality of CUQIpy.
CUQIpy is part of the CUQI project supported by the Villum Foundation.
Quick Links: Installation | Tutorials | How-To Guides | Source Repository | 🔌 CUQIpy Plugins
🧪 Quick Example - UQ in a few lines of code#
Experience the simplicity and power of CUQIpy with this Image deconvolution example. Getting started with UQ takes just a few lines of code:
# Imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from cuqi.testproblem import Deconvolution2D
from cuqi.distribution import Gaussian, LMRF, Gamma
from cuqi.problem import BayesianProblem
# Step 1: Set up forward model and data, y = Ax
A, y_data, info = Deconvolution2D(dim=256, phantom="cookie").get_components()
# Step 2: Define distributions for parameters
d = Gamma(1, 1e-4)
s = Gamma(1, 1e-4)
x = LMRF(0, lambda d: 1/d, geometry=A.domain_geometry)
y = Gaussian(A@x, lambda s: 1/s)
# Step 3: Combine into Bayesian Problem and sample posterior
BP = BayesianProblem(y, x, d, s)
BP.set_data(y=y_data)
samples = BP.sample_posterior(200)
# Step 4: Analyze results
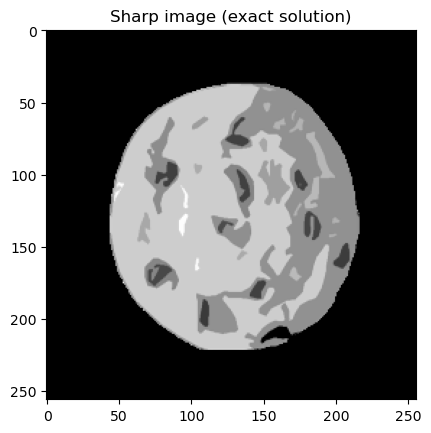
info.exactSolution.plot(); plt.title("Sharp image (exact solution)")
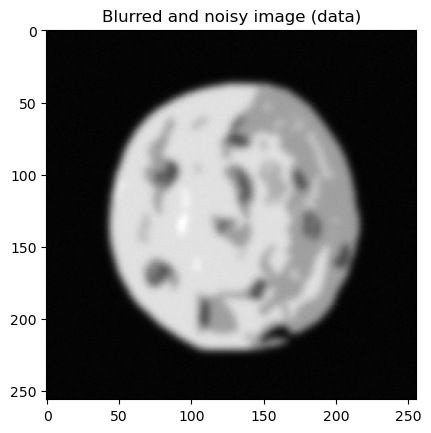
y_data.plot(); plt.title("Blurred and noisy image (data)")
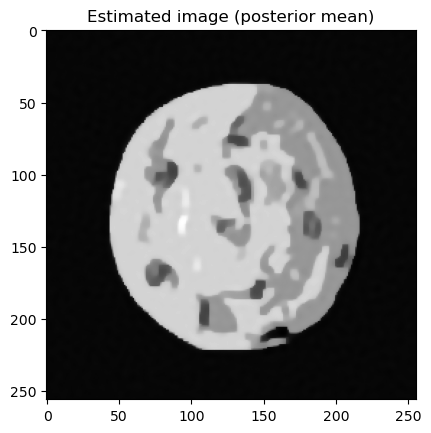
samples["x"].plot_mean(); plt.title("Estimated image (posterior mean)")
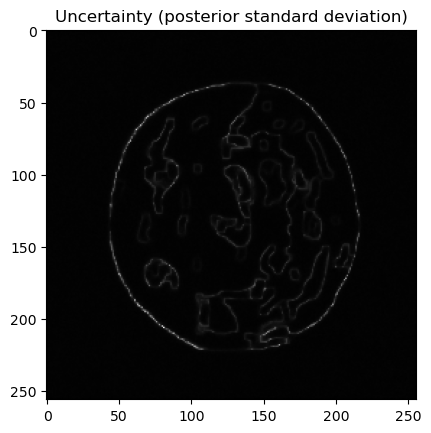
samples["x"].plot_std(); plt.title("Uncertainty (posterior standard deviation)")
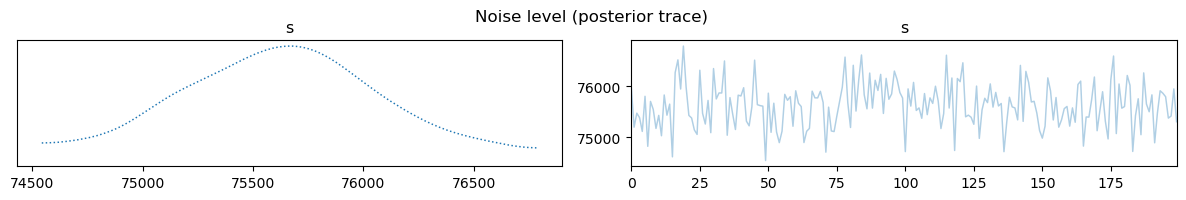
samples["s"].plot_trace(); plt.suptitle("Noise level (posterior trace)")
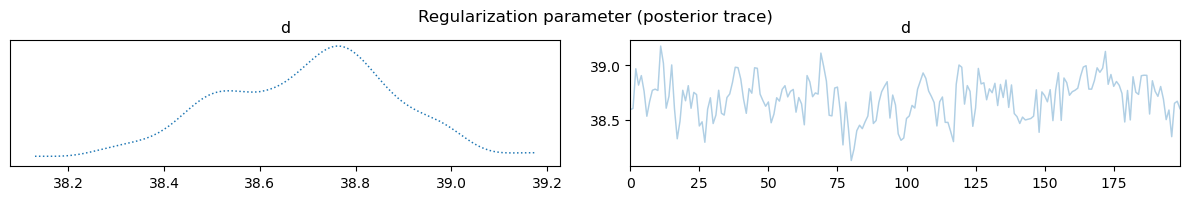
samples["d"].plot_trace(); plt.suptitle("Regularization parameter (posterior trace)")



🔌 CUQIpy Plugins#
A number of plugins are available as separate packages that expand the functionality of CUQIpy:
CUQIpy-CIL: A plugin for the Core Imaging Library (CIL) providing access to forward models for X-ray computed tomography.
CUQIpy-FEniCS: A plugin providing access to the finite element modelling tool FEniCS, which is used for solving PDE-based inverse problems.
CUQIpy-PyTorch: A plugin providing access to the automatic differentiation framework of PyTorch within CUQIpy. It allows gradient-based sampling methods without manually providing derivative information of distributions and forward models.
🌟 Contributors#
A big shoutout to our passionate team! Discover the talented individuals behind CUQIpy here.